The History of WiFi: Exploring the Evolution of Wireless Connectivity
When was WiFi invented? Have you ever wondered how this technology came into existence? It’s our go-to for making decisions, getting answers, researching specific topics, and speeding up work. It allows you to buy groceries without going to a store and even hire taxis without leaving the house.
This technology even lets you video call people you know, thousands of miles away, in real-time. If you’re old enough, you’ll remember a time before WiFi was universally available. In the old days, there was the good old dial-up internet. It was painfully slow and stopped working when you called someone via your landline.
So, when was WiFi discovered? The history of WiFi is fascinating because incredible people have been contributing to its development for over a century. Let’s go back to the origin of WiFi and see its evolution over the years.

The Origins of Wireless Technology
To understand when was wireless internet invented, we need to look at a different era, i.e., between the 19th and 20th centuries. During this period, scientists were still proving that radio signals could travel through the air without wires.
Early Theories and Discoveries
Our first stop in answering when was WiFi created was in the 19th century, specifically the late 1880s. Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, a German physicist, conducted several experiments to show that electromagnetic waves were real.
He continued the work of James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish physicist. James had already created a framework predicting the behavior of electromagnetic waves. The work of these two fine gentlemen became the foundation for wireless communications.
Pioneering Wireless Technologies
The next stop in the WiFi timeline is the late 19th century. Several inventors were trying to make wireless technologies a reality. However, the breakthrough we are looking for came from Guglielmo Marconi in 1895. He managed to transmit radio waves over a distance of 1.5 miles (2.4 kilometers), the first practical use of radio frequencies for wireless communication.
Imagine, before that, all data traveled only through wires, and then — boom! The radio signals flew right through the air.
He continued refining his systems and eventually transmitted radio signals across the Atlantic Ocean, i.e., over 1800 miles. The inventor won a Nobel Prize for his work in wireless telegraphy. This is the first real step towards WiFi creation.
He started the Wireless and Telegraph Signal Company in July 1897. In 1899, the company changed its name to the Marconi Company. The inventor was instrumental in helping commercial ships communicate with coastal stations.
In 1900, he developed a special circuit for tuning radio wave frequencies and received a patent for his invention. These systems were crucial in showing that reliably sending information through the air was possible. This, in a way, kickstarted the concept of wireless networks, eventually leading to the creation of WiFi.
The Blueprint for Modern WiFi
Inventors and scientists demonstrated that wireless communication is possible. But we are still a long way from creating WiFi. Where was WiFi invented? Let’s learn about modern developments that became the blueprint for the technology we know today to answer this question.
Groundbreaking Inventions
How was WiFi invented? When looking for an answer, you’ll hear about Hedy Lamarr, a Hollywood actress, and George Antheil, a composer. The duo sought ways to help the Allies during World War II. They discovered frequency hopping to prevent the enemy from jamming torpedoes.
Instead of sending a radio signal over a single frequency, it would jump between several frequencies.
Frequency hopping reduces interference from other signals and makes it harder for bad actors to intercept the signals. For the military and civilians, these benefits provide a significant advantage over their enemies.
The navy rejected the concept because it didn’t seem feasible at the time. However, this was the foundation for wireless technologies like Bluetooth, GPS, and WiFi.
So, where does WiFi come from? Well, you have only one part of the answer. Let’s fast forward to the 1990s to get the second part of the answer.
Dr. John O’ Sullivan worked with researchers from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization of Australia (CSIRO). They were at the Dwingeloo Radio Observatory, trying to catch signals from black holes.
They developed Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), an important discovery that made wireless networks inside buildings possible. When did WiFi come out to the public? Well, this was only possible due to the work of Sullivan and his team.

The Birth of ALOHAnet
Perhaps we went a little too far ahead because there’s another critical WiFi creation contribution. This is the ALOHAnet, launched in 1971 by Professor Norman Abramson from the University of Hawaii. They used the radio wave spectrum to connect all the campuses in the islands.
In a way, this was the first WiFi.
Although ALOHAnet had several limitations, it was the first real example of a wireless network made for data transmission. In 1971, ALOHAnet joined ARPANET, enabling computers to communicate wirelessly across the U.S.
Why was WiFi invented? The goal was to allow the transmission of data without relying on cables. However, its discovery was accidental because researchers and scientists were focusing on solving other problems.
The Road to Standardization
And the story about how was WiFi made goes on. WiFi, as a standalone technology, was incredible. However, without standards, it may not have been widely adopted.
Thankfully, several bright minds were already working on solving this problem. The standards they created made WiFi fast, reliable, and compatible with all internet-based products.
The Role of IEEE and Early Standards
When did WiFi become popular? This happened due to the efforts of Vic Hayes, the chairman of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). He is also the father of WiFi. He and his team focused on standardizing WiFi technology.
It wasn’t easy to convince everyone to follow a standard. Thanks to Vic’s persistence, he convinced everyone, including European regulators, to agree on:
An 83.5 MHz radio band for the 2.4 GHz frequency A 475 MHz radio band for the 5 GHz frequency
In 1997, they developed 802.11, the earliest standard for WiFi. This lets devices send data wirelessly over the 2.4 GHz band. The speed, at the time, was a groundbreaking 2 Mbps. Sounds extremely slow nowadays, but back then, it was revolutionary. This is, essentially, the WiFi invention date.
In 1999, 802.11b, a better standard, showed up. It was much faster, i.e., up to 11 Mbps. Reliability and speed were the biggest problems with these standards. However, they enabled devices from different manufacturers to talk to one another wirelessly.
When was WiFi popularized? It happened after Hayes’ work to introduce worldwide standards.

The Birth of the WiFi Brand
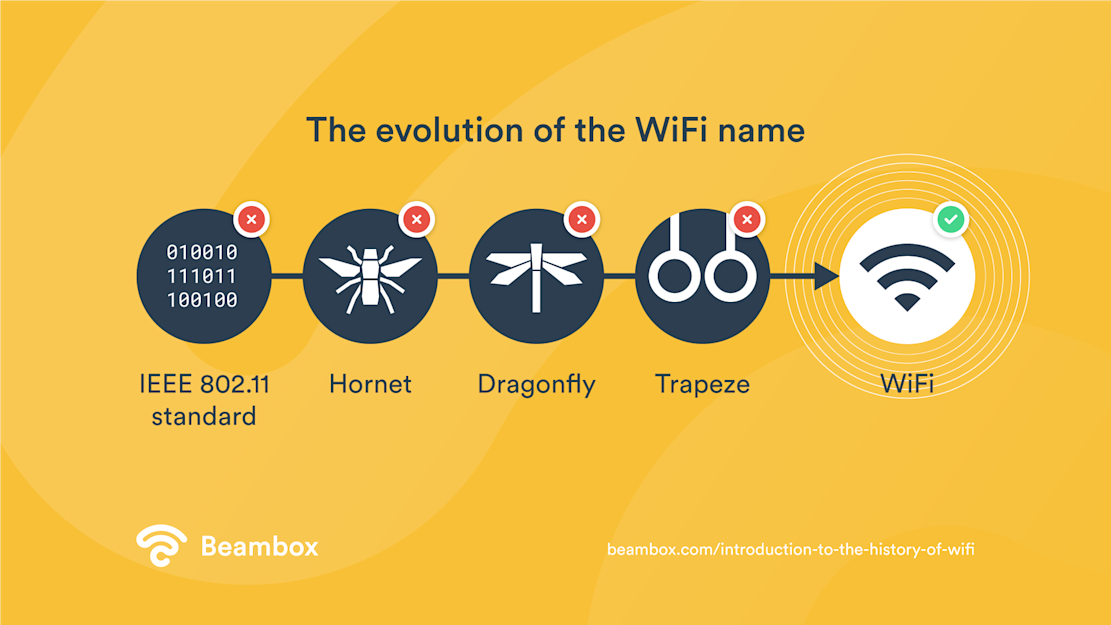
Now, let’s focus on, ‘when did WiFi start?’ 802.11b isn’t exactly catchy, nor does it roll off the tongue. The name of this wireless technology comes from the Wi-Fi Alliance, formed in 1999. Initially, they thought of using ‘Dragonfly’ and ‘Trapeze,’ but they settled on WiFi. This was similar to Hi-Fi and easy to remember.
What does WiFi stand for? It actually doesn’t have any meaning.
They own the trademark for Wi-Fi Certified, which lets consumers and businesses know the devices are interoperable and backward compatible. What do these terms mean? That’s a good question.
Interoperability indicates that the devices can work with various equipment from different manufacturers. Backward compatibility indicates that newer devices can work with older equipment.
And how old is WiFi? Well, the name showed up in 1999, which means it’s old enough to drive a car.
Evolution of WiFi: Decades of Innovation
We’ve already talked about how was WiFi discovered. Now, let’s quickly go through the evolution of this technology over several decades.
The FCC’s Approval of ISM Bands (1985)
The U.S. Federal Communications Commission approved using 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz without licenses for the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) radio frequency bands.
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz will feel familiar because you may have seen these options in your router. This is what’s different between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz:
2.4 GHz has incredible range, but at the cost of speed. 5 GHz is significantly faster, but doesn’t have the range of 2.4 GHz.
Thankfully, almost every modern router uses both frequencies, so you can use what’s convenient and works best for you.
The Introduction of 802.11 (1997)
The 802.11 standard by Vic Hayes and the IEEE paved the way for WiFi. The first standard wasn’t widely adopted because it was slow, i.e., 2 Mbit/s. However, it became the foundation for future standards.
The WiFi Alliance (1999)
The Wi-Fi Alliance came up with the name’ WiFi.’ They also certified devices to ensure compatibility with the WiFi networks. Their efforts enabled widespread adoption of WiFi, which is why you will find this technology everywhere.
When did WiFi routers come out? Here’s a hint — it happened in the same year as the WiFi Alliance. If you haven’t already guessed the answer, it’s 1999.
Major Protocol Releases
How long has WiFi been around? Well, it’s been with us for more than two decades. And during this period, each new WiFi protocol changed the wireless network technology for the better. Here’s how:
- 802.11b (1999): This standard increased the speed to 11 Mbps and was widely adopted. When did WiFi come out in homes? It was around 1999 that WiFi became popular in households everywhere.
- 802.11a (1999): The 802.11a was faster than 802.11b since it offered speeds up to 54 Mbps. It also operated at a different frequency, i.e., 5 GHz. However, this reduced the range of the WiFi signal. Plus, it was harder for these signals to pass through thick obstacles.
- 802.11g (2003): 802.11g combined the best of 802.11b and 802.11a. It increased the speed from 2.4 GHz to 54 Mbps, ensuring backward compatibility with older hardware. When did WiFi become common? It was after this year because of the significant technological improvements.
- 802.11n (2009): With the 802.11n standard came Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO). This technology allowed several antennas to send and receive data wirelessly. It improved the signal strength and speed.
- 802.11ac (2013): The 802.11ac standard was a game changer. It introduced gigabit speeds, enabling large file transfers and high-quality video streaming.
- 802.11ax (WiFi 6, 2019): The 802.11ax is a recent standard available in most routers and devices today. It enabled routers to talk to multiple devices simultaneously. This is why smart homes and devices can function and remain connected to the internet.
The Rise of Mobile Devices and the Demand for WiFi Speed
You can see how every contribution led to the invention of WiFi. But there’s more. The growing popularity of mobile devices, especially during the 2000s and 2010s, increased the demand for reliable and faster WiFi.
As people started using their smartphones to do everything, the focus shifted towards improving WiFi technology. The 802.11 standard and the improvements from 802.11b to 802.11ac satisfied this growing demand.
Transition to the Modern Era of WiFi
The WiFi you see today is far from what it was since its inception in the 1990s. Two major drivers helped with the WiFi evolution to make the transition to the modern era of WiFi.
The Impact of Smartphones
The first driver, to no one’s surprise, is smartphones. Brands like Samsung, Huawei, LG, Motorola, and HTC sold billions of smartphones globally.
These devices require a constant connection to the Internet. People were using them for pretty much everything, and WiFi protocols needed to be significantly improved to keep up.
The Growing Number of Connected Devices
The second driver of demand was due to the growing number of devices with an internet connection. Initially, there was the Internet of Things (IOT). These were devices that could connect to the internet for various tasks. For example, controlling your smart light through an app is possible because of WiFi.
Nowadays, countless devices, including microwaves, refrigerators, washing machines, TVs, speakers, and more, have internet access.
It’s a no-brainer that the more devices that come online, the more congested these wireless networks become. As a result, WiFi protocols kept evolving to provide a better experience without any slowdowns or connection issues.
Innovations in WiFi Technology
WiFi never stands still — it’s constantly changing and getting better with every new standard. Every few years, there’s a significant leap in internet speeds and reliability. Let’s look at how these innovations are changing the world of wireless networks.
Advancements in WiFi 6 and 6E
Inventors like Matt Perry from Broadcom and an army of engineers created the WiFi 6 and 6E standards. These technologies enable faster speeds with lower latencies while remaining efficient.
This is why your phone, laptop, and smartwatch can talk to one another and use the internet without interference.
The Potential of WiFi 7
WiFi 7 will take another significant leap and improve wireless networks. It will improve on latency and speed, which is a given. This tech will also allow devices to connect to multiple WiFi frequencies, substantially improving reliability.
WiFi 7 will benefit applications requiring high bandwidth, such as AR, VR, and 4K and 8K video streaming.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite all the innovations, WiFi is still facing serious challenges. As more devices come online every day, the demand for WiFi will continue to grow.
Addressing Overcrowding and Interference
The biggest problems with wireless networks are overcrowding and interference. You may have already experienced this. For example, let’s say you use the 5 GHz frequency in a house with thick walls. The further you move away from the router, the more unstable the connection becomes.
Similarly, apartment complexes have significant interference due to the number of wireless network devices. One option is to switch to a different channel, which will alleviate some of the interference problems.
Thankfully, manufacturers are developing new technologies and standards to overcome these issues.
The Role of AI and Enhanced Networking Technology
Since 2018, artificial intelligence has seriously started helping WiFi work better. Big companies like Cisco, Google, and Huawei have been creating systems that learn how you use the internet.
For example, AI spots “traffic jams” in the network and finds the fastest routes for your data. This helps make WiFi considerably quicker, especially when you have dozens of devices at home.
In 2019, Google figured out how to automatically switch devices to the best channels. This way, the signal won’t glitch or face interference due to other networks.
Huawei isn’t far behind. Their routers can predict when your internet usage will peak and “speed up” the traffic so everything runs smoothly.
And here’s another cool thing — AI helps protect WiFi from hacks.
So, AI is like a smart assistant for your WiFi, making it faster, more stable, and safer. And this is just the beginning.
As a business, it’s become a necessity to provide WiFi in your establishment. If you don’t have WiFi, your customers will shop elsewhere. Beambox makes it easy to provide free WiFi to your patrons. The best part? You can even convert your wireless network into a revenue stream.
How? We can turn this utility into a marketing asset, helping you collect valuable customer information. This can improve your advertising campaigns and promote your social media profiles.
Contact Beambox today to learn how to make your WiFi an invaluable resource for your business!



